The Beginning of ERP: Prologue to Enterprise Resource Planning
Welcome, dear readers, to a journey back in time to explore the origins of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. In order to fully understand the complexity and importance of these systems in today’s business world, we must first delve into the prologue of ERP. Let us embark on this enlightening adventure together as we uncover the beginnings of ERP and its evolution into the powerful tool it is today.
Evolution of ERP Systems
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems have come a long way since their inception in the 1960s. Initially, ERP systems were designed to automate manual business processes within individual departments such as accounting, finance, and human resources. These early systems were limited in scope and functionality, with each department working in isolation and utilizing its own software to manage specific tasks.
As technology advanced, so did ERP systems. In the 1990s, ERP systems evolved to integrate all departments within an organization, allowing for real-time data sharing and collaboration between different functions. This shift towards integrated systems marked the beginning of what we now know as modern ERP systems.
With the rise of the internet and cloud computing, ERP systems became even more powerful and accessible. Cloud-based ERP systems allow for remote access, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for businesses of all sizes. In addition, the integration of mobile technologies has further revolutionized ERP systems, enabling employees to access critical data and collaborate on-the-go.
Today, ERP systems have evolved beyond just automating business processes. They now offer advanced features such as predictive analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions and stay ahead of the competition. Furthermore, ERP systems are now customizable to meet the specific needs of different industries, offering modules for manufacturing, commerce, supply chain management, and more.
The future of ERP systems is bright, with continued advancements in technology shaping the way businesses operate. Trends such as Industry 4.0, IoT (Internet of Things), and blockchain are being integrated into ERP systems, making them even more powerful and efficient. As businesses continue to adapt to a rapidly changing global market, ERP systems will play a crucial role in streamlining operations, improving productivity, and driving growth.
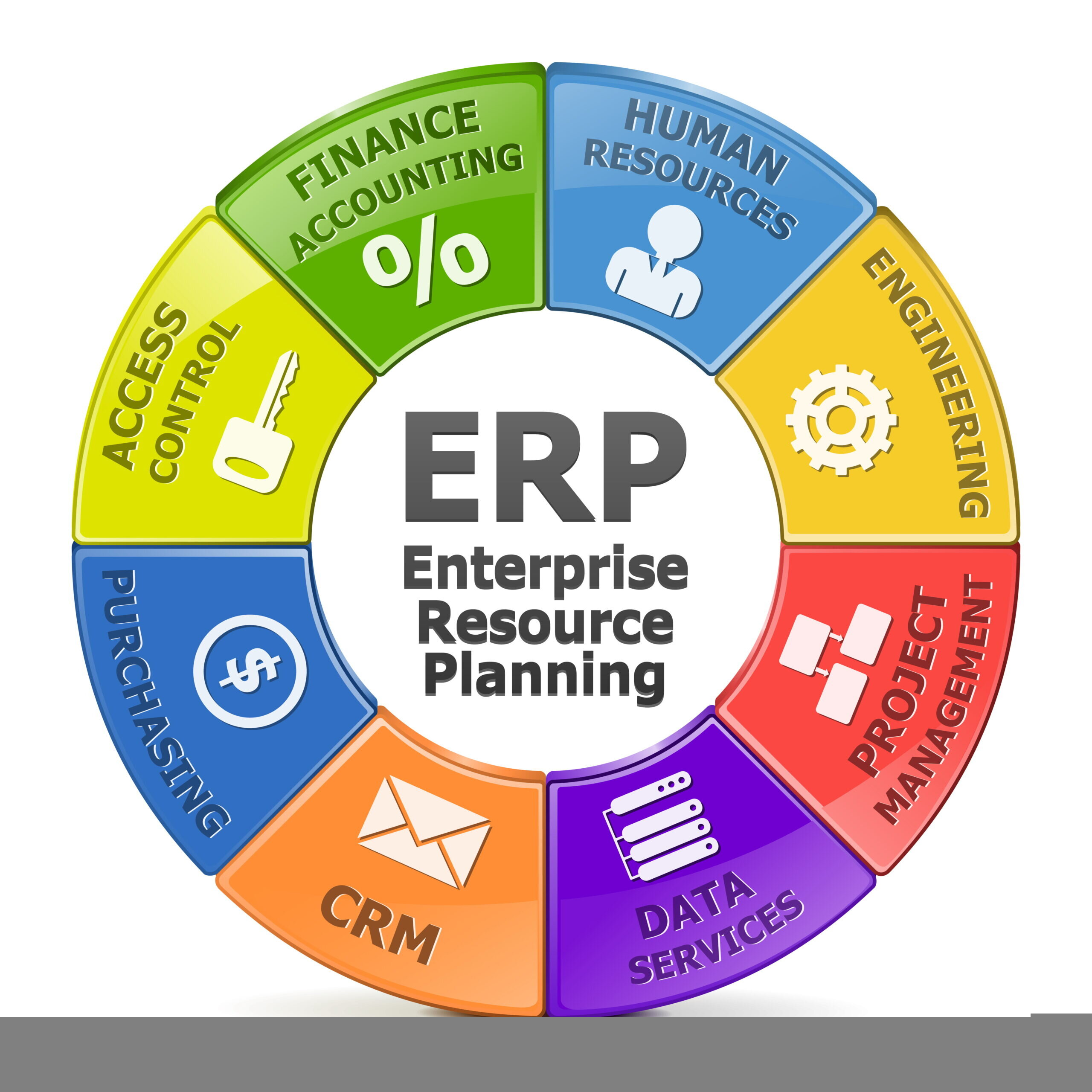
Key Components of ERP Software
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a powerful tool that integrates all the important functions of a business into a single system. This centralized system streamlines processes, increases efficiency, and ensures data accuracy across departments. There are several key components that make up ERP software, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the system.
1. Accounting and Finance: One of the core components of ERP software is its ability to manage financial data and transactions. This includes accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting. By centralizing financial information, businesses can gain a comprehensive view of their financial health and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
2. Human Resources: Another important component of ERP software is its human resources module, which helps organizations manage their employees’ information, payroll, benefits, training, and performance evaluations. This module streamlines HR processes and ensures compliance with labor laws and regulations. It also helps businesses optimize their workforce and improve employee satisfaction and retention.
3. Inventory Management: ERP software includes an inventory management module that helps businesses track and manage their inventory levels, orders, and shipments. This module provides real-time visibility into stock levels, optimizes inventory levels, and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking. By effectively managing inventory, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
4. Supply Chain Management: ERP software also includes a supply chain management module that helps businesses optimize their supply chain processes, from procurement to distribution. This module streamlines supplier management, order fulfillment, logistics, and demand planning. By synchronizing supply chain activities, businesses can reduce lead times, improve efficiency, and enhance collaboration with suppliers and partners.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Another key component of ERP software is its CRM module, which helps businesses manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, marketing campaigns, and customer service. This module allows businesses to track customer interactions, analyze customer data, and personalize marketing and sales efforts. By effectively managing customer relationships, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
6. Reporting and Analytics: ERP software includes reporting and analytics tools that allow businesses to generate customized reports, dashboards, and insights based on real-time data. These tools help businesses monitor performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging reporting and analytics, businesses can optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
Overall, ERP software is a comprehensive solution that integrates key components such as accounting and finance, human resources, inventory management, supply chain management, CRM, and reporting and analytics. By leveraging these components, businesses can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and drive growth in today’s competitive business landscape.
Implementation Process of ERP Systems
Implementing an ERP system is no easy feat and requires a detailed and well-thought-out process. The first step in this process is identifying the needs and requirements of the organization. This involves reviewing current business processes, identifying gaps in functionality, and understanding the goals and objectives of the company. Once these have been established, the next step is to select a suitable ERP system that aligns with these needs and requirements.
After selecting the ERP system, the implementation team is assembled. This team typically consists of key stakeholders from various departments within the organization, including IT, finance, operations, and human resources. It is crucial to have representation from each department to ensure that the implementation process addresses the needs of the entire organization.
Once the implementation team is in place, the next step is to define the project scope and timeline. This involves outlining the key milestones, deliverables, and deadlines for the implementation process. It is essential to set realistic expectations and ensure that the project scope is well-defined to avoid scope creep and delays.
With the project scope and timeline in place, the next step is to prepare for the implementation process. This involves data migration, system configuration, and training. Data migration is crucial as it involves transferring existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. System configuration involves setting up the ERP system according to the organization’s needs and requirements. Training is also essential to ensure that end-users are familiar with the new system and can use it effectively.
Once the system is configured and users are trained, the next step is to test the system. This involves conducting various tests to ensure that the system functions as intended and meets the needs of the organization. Testing is a crucial step in the implementation process as it helps identify any issues or bugs that need to be addressed before the system goes live.
After testing is complete, the final step is to go live with the ERP system. This involves migrating all data and processes to the new system and transitioning from the old system to the new one. It is essential to have a detailed plan in place for the go-live process to minimize disruptions to the business and ensure a smooth transition.
In conclusion, the implementation process of ERP systems is a complex and involved process that requires careful planning and coordination. By following these steps and working closely with the implementation team, organizations can successfully implement an ERP system that meets their needs and improves business processes.
Benefits of Using ERP Software
ERP, or enterprise resource planning, software is a powerful tool that integrates various business functions into one comprehensive system. There are numerous benefits to using ERP software in your organization, ranging from increased efficiency to improved decision-making capabilities. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of implementing ERP software:
1. Streamlined Processes: One of the primary benefits of using ERP software is the streamlining of business processes. With all departments and functions integrated into a single system, communication and data sharing become much more efficient. This leads to a reduction in manual tasks, eliminating the need for duplicate data entry and minimizing the chance of errors.
2. Improved Visibility: ERP software provides real-time visibility into all aspects of your business operations. From inventory levels to sales performance, you can access up-to-date information at any time. This visibility enables better decision-making, as managers can quickly identify trends, spot potential issues, and make adjustments as needed.
3. Enhanced Collaboration: By centralizing data and processes, ERP software promotes collaboration across different departments and teams. Employees can access the information they need to work more effectively together, leading to increased productivity and better outcomes. Additionally, with everyone working from a single source of truth, there is less room for miscommunication or misunderstandings.
4. Customization and Scalability: One of the key advantages of ERP software is its flexibility and scalability. Most ERP systems can be customized to meet the specific needs of your business, whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise. As your business grows or changes, the ERP software can easily be adjusted to accommodate new requirements. This ensures that your system remains relevant and continues to support your business goals over time.
In conclusion, the benefits of using ERP software are wide-ranging and can have a significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of your organization. From streamlining processes and improving visibility to promoting collaboration and offering customization options, ERP software is a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. If you haven’t already implemented ERP software in your organization, now might be the time to consider making the investment for long-term success.
Future Trends in ERP Technology
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the future of ERP systems is filled with exciting possibilities. Here are some of the trends that are expected to shape the future of ERP technology:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are expected to play a major role in the future of ERP technology. By analyzing large amounts of data and identifying patterns, AI can provide valuable insights that can help businesses make informed decisions and streamline their processes. Machine learning algorithms can help ERP systems become more intelligent and adaptive, allowing them to predict future trends and make proactive recommendations.
2. Internet of Things (IoT): The Internet of Things (IoT) is already transforming the way businesses operate, and its impact on ERP systems is expected to grow in the future. By connecting physical devices and sensors to ERP systems, businesses can gather real-time data on their operations and make more informed decisions. For example, IoT-enabled ERP systems can track the location and condition of assets in real-time, optimize supply chain management, and improve maintenance processes.
3. Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based ERP systems is expected to continue in the future. Cloud computing offers several advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By hosting their ERP systems in the cloud, businesses can access their data and applications from anywhere, at any time. This allows for greater collaboration among employees, improved data security, and easier system updates and maintenance.
4. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way ERP systems handle transactions and data security. By creating a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger of transactions, blockchain technology can enhance the trustworthiness of ERP systems and reduce the risk of fraud. Blockchain can also improve data integrity and transparency, making it easier for businesses to track the flow of information within their ERP systems.
5. Personalization and User Experience: In the future, ERP systems are expected to focus more on providing personalized experiences for users. This includes customizing the interface, workflow, and functionality of the ERP system to meet the specific needs of each user. By tailoring the user experience to individual preferences, businesses can improve employee satisfaction, productivity, and overall system adoption.
Overall, the future of ERP technology is bright, with exciting advancements on the horizon. By embracing these trends and technologies, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and drive growth and innovation in their operations.